Brain Lobes And Their Functions Pdf
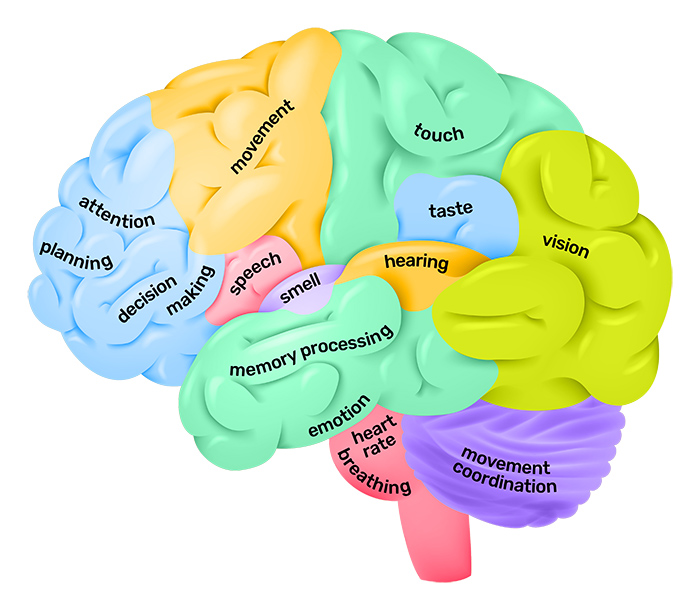
MedicalRF.com/Getty Images The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain that functions to make human beings unique. Distinctly human traits including higher thought, language and human as well as the ability to think, reason and imagine all originate in the cerebral cortex. The cerebral cortex is what we see when we look at the brain. It is the outermost portion that can be divided into the four lobes of the brain. Each bump on the surface of the brain is known as a gyrus, while each groove is known as a sulcus.
PIXOLOGICSTUDIO/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY / Getty Images The cerebral cortex can be divided into four sections, which are known as lobes (see image). The frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe have been associated with different functions ranging from reasoning to auditory perception. The frontal lobe is located at the and is associated with reasoning, motor skills, higher level cognition, and expressive language.
- Functions such as breathing. Anatomy of the Brain Figure 1. Eight bones form the skull and. Lobes of the brain.
- The Human Brain - Structure and Function Lessons from History Paul Broca. Injuries to a small area in the frontal lobe of the cortex on the left hemisphere.
At the back of the frontal lobe, near the central sulcus, lies the motor cortex. This area of the brain receives information from various lobes of the brain and utilizes this information to carry out body movements. Damage to the frontal lobe can lead to changes in sexual habits, socialization, and attention as well as increased risk-taking. The parietal lobe is located in the middle section of the brain and is associated with processing tactile sensory information such as pressure, touch, and pain. A portion of the brain known as the somatosensory cortex is located in this lobe and is essential to the processing of the body's senses. The temporal lobe is located on the bottom section of the brain.
• The Parietal lobes are responsible for Spatial functions. •Their irritability is not only due to fatigue. Less tissue in parts of the brain's.

This lobe is also the location of the primary auditory cortex, which is important for interpreting sounds and the language we hear. The is also located in the temporal lobe, which is why this portion of the brain is also heavily associated with the formation of. Damage to the temporal lobe can lead to problems with memory, speech perception, and language skills. The occipital lobe is located at the back portion of the brain and is associated with interpreting visual stimuli and information.
The primary visual cortex, which receives and interprets information from the retinas of the eyes, is located in the occipital lobe. Damage to this lobe can cause visual problems such as difficulty recognizing objects, an inability to identify colors, and trouble recognizing words.
Main article: The frontal lobe is located at the front of each and positioned in front of the and above and in front of the. It is separated from parietal lobe by a space between tissues called the, and from the temporal lobe by a deep fold called the also called the Sylvian fissure. The, forming the posterior border of the frontal lobe, contains the, which controls voluntary movements of specific body parts. The frontal lobe contains most of the -delicate in the. The dopamine system is associated with, tasks, and. Dopamine tends to limit and select arriving from the to the.
A report from the says a variant that reduces dopamine activity in the is related to poorer performance and inefficient functioning of that brain region during working memory tasks, and to a slightly increased risk for. Parietal lobe. Main article: The parietal lobe is positioned above the and behind the and. The parietal lobe integrates information among various, including spatial sense and navigation , the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch in the which is just posterior to the central sulcus in the, and the of the. The major sensory inputs from the (, and receptors), relay through the to the parietal lobe. Several areas of the parietal lobe are important in. The somatosensory cortex can be illustrated as a distorted figure — the (: 'little man'), in which the body parts are rendered according to how much of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to them.
The superior parietal lobule and inferior parietal lobule are the primary areas of body or spatial awareness. A lesion commonly in the right superior or inferior parietal lobule leads to. Occipital lobe. Main article: The occipital lobe is the of the containing most of the anatomical region of the. The is, commonly called V1 (visual one). Human V1 is located on the side of the occipital lobe within the; the full extent of V1 often continues onto the posterior pole of the occipital lobe. V1 is often also called striate cortex because it can be identified by a large stripe of myelin, the.
Visually driven regions outside V1 are called. There are many extrastriate regions, and these are specialized for different visual tasks, such as visuospatial processing, color differentiation, and motion perception. Temporal lobe. Main article: The insular cortex is a portion of the folded deep within the (the fissure separating the from the and ). The insulae are believed to be involved in and play a role in diverse functions usually linked to or the regulation of the body's. These functions include, and.
In relation to these, it is involved in. The insular cortex is divided into two parts: the larger anterior insula and the smaller posterior insula in which more than a dozen field areas have been identified. The cortical area overlying the insula toward the lateral surface of the brain is the (meaning lid). The opercula are formed from parts of the enclosing frontal, temporal, and parietal lobes.
Additional images. Guilherme Carvalhal Ribas (2010). “The Cerebral Sulci and Gyri”.
Neurosurg Focus 56 (2): E2. National Institute of Mental Health. May 29, 2001. Archived from on April 4, 2015. Retrieved 2013-06-20. Schacter, D.

L., Gilbert, D. New Work (NY): Worth Publishers.
Archived from on 2007-12-31. Retrieved 2008-02-27. Rice University. Retrieved 2 January 2011. Smith; Kosslyn (2007). Cognitive Psychology: Mind and Brain.
New Jersey: Prentice Hall. Pp. 21, 194–199, 349. Fix, JD (2008).
I've been a game critic for the past eleven years, and I grew up with the Biker Mice. Biker mice from mars pc game. I had played both commercially available Biker Mice games and I will say that this one has the edge over the DS version.
Brain Lobes And Their Jobs
Neuroanatomy (fourth ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. External links Wikimedia Commons has media related to.
Top Pages
- Crisis Core Walkthrough Pdf
- Dualshock 3 Windows 7 Driver
- Turbo 264 Hd Activation Key
- La Sera Sees The Light Rar
- Music Maker Soundtrack Edition
- Drivers Vs-pvr-tv 7134se
- A Era Do Vazio Gilles Lipovetsky Pdf
- Sims 3 Asian Face Mods Skyrim
- Pokemon Ruby Randomizer Gba
- Lenovo Wan Miniport Drivers Windows 8
- Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 For Windows 7 Home Basic
- Vso Er Ultimate 3 0 2 0 Portable Bottle
- Delphi 7 For Windows 7 64 Bit
- El Burgues Gentilhombre Pdf Gratis
- La Chevaliere Seth Gueko Games
- Just Wright Full Movie For
- Legacy Of Kain Soul Reaver 1 Iso





